This policy brief containing general as well as sector specific recommendations for Government action is the product of collaborative efforts of several organisations, academicians, practitioners, and experts working in the area of child rights. Members of the following networks and alliances contributed to this policy brief: Alliance for Right to ECD, Covid Response Alliance of India on Child Protection (CRAICP), India Alternative Care Network (IACN), ProChild Coalition, Right to Education Forum, Right to Food Campaign, Working Group on Human Rights to India and the UN (WGHR). They worked in thematic sub-groups to develop sector specific recommendations which were integrated in the form of this brief to represent the core minimum demands from the State to ensure children’s rights during COVID-19. The list of 212 individuals and organisations that have endorsed the Policy Brief are included on page 19.
projects
RIGHTS OF CHILDREN IN THE TIME OF COVID-19
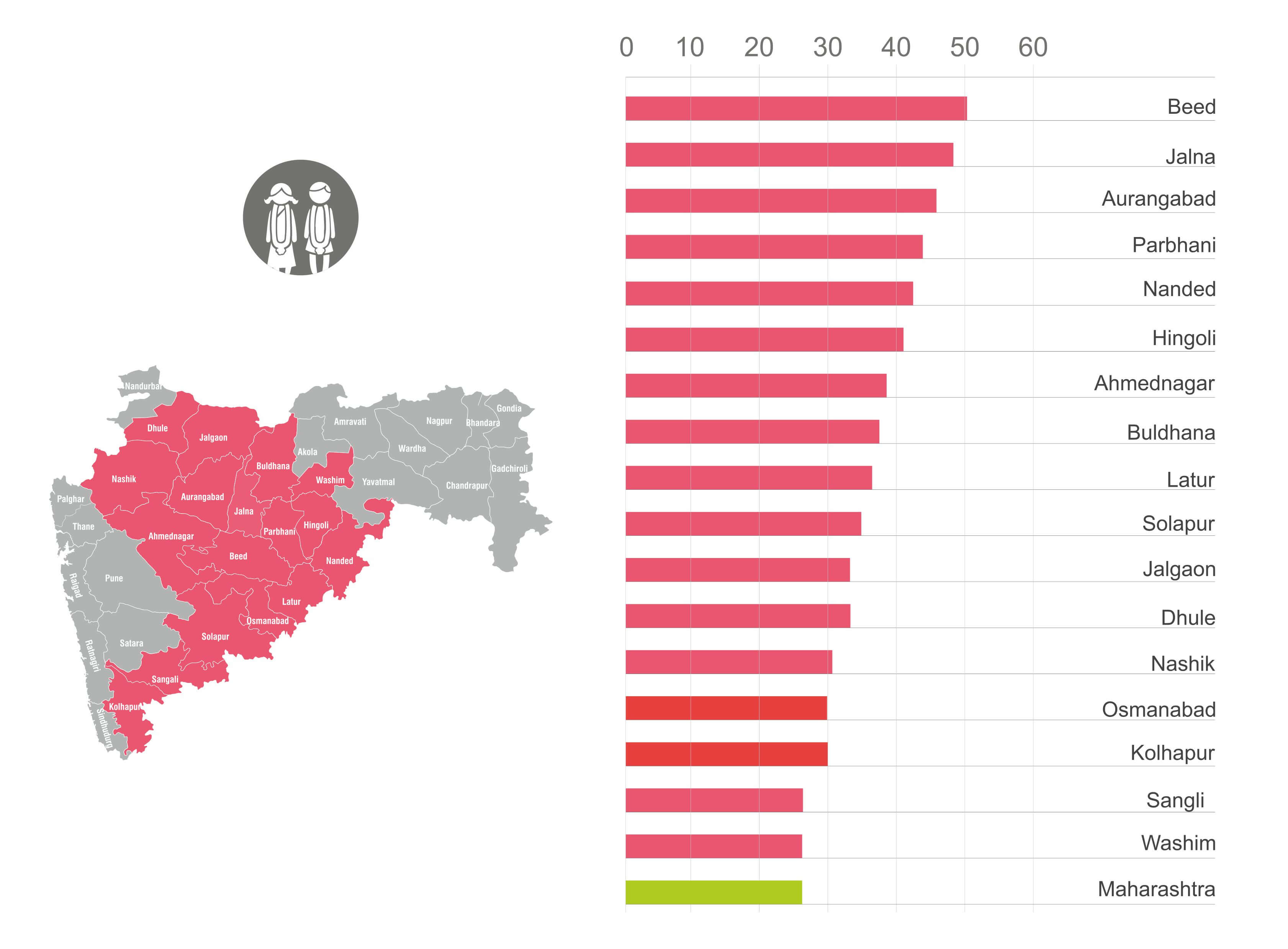
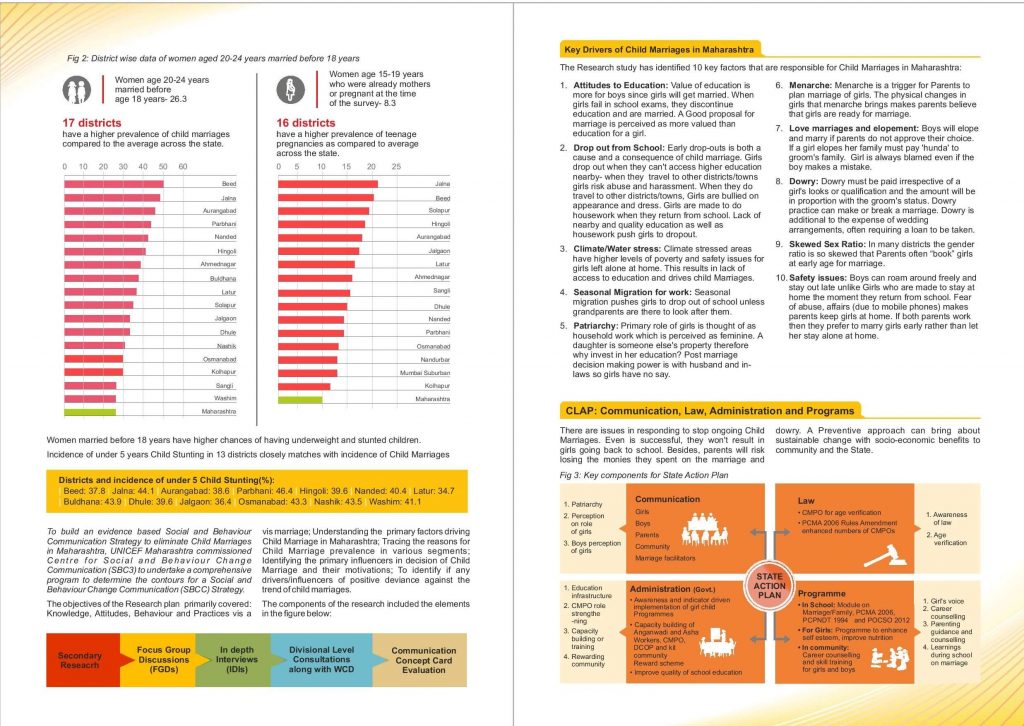
Fig 2. 17 districts have a higher prevalence of child marriages compared to the average across the state
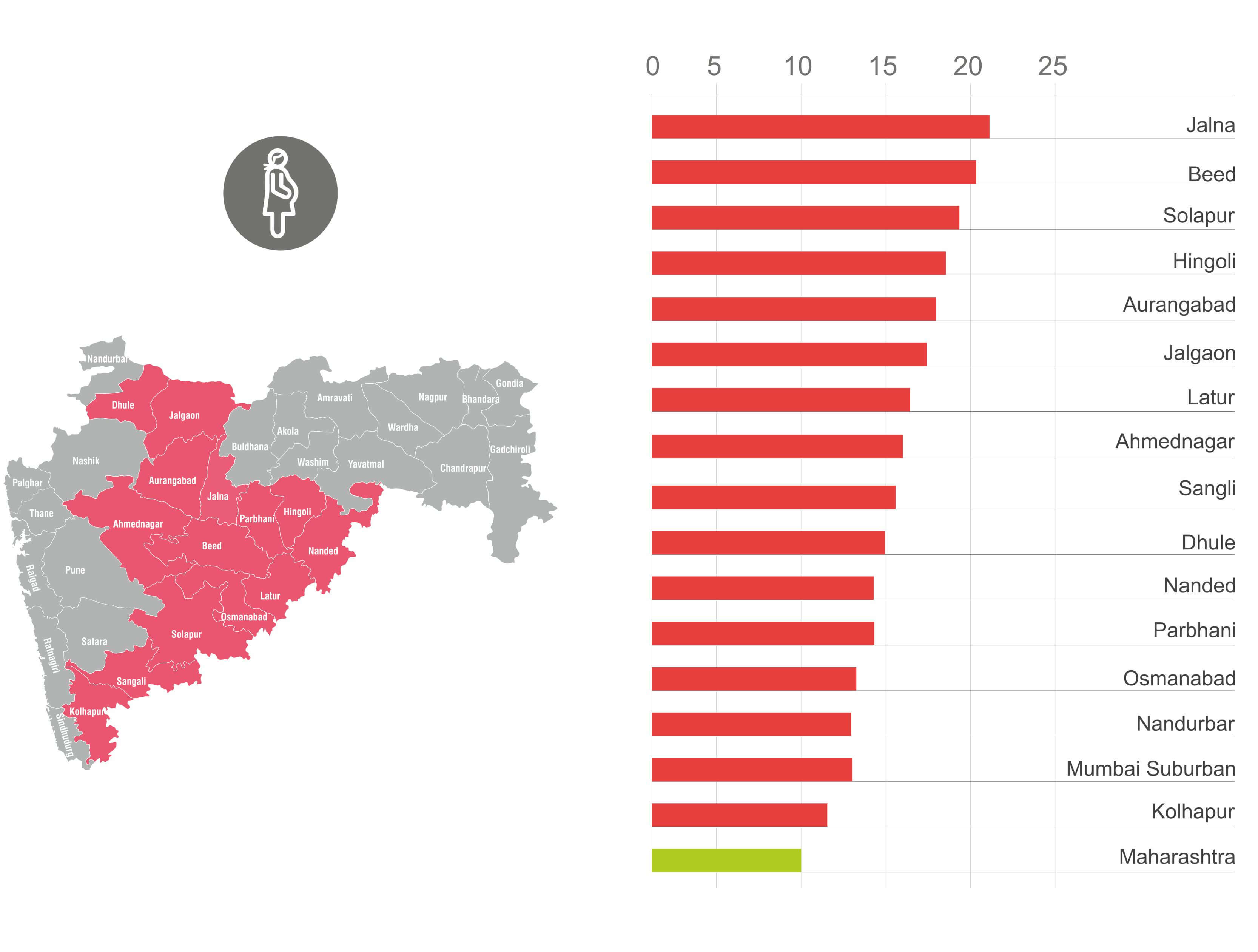
Fig 3. 16 districts have a higher prevalence of teenage pregnancies as compared to average across the state.
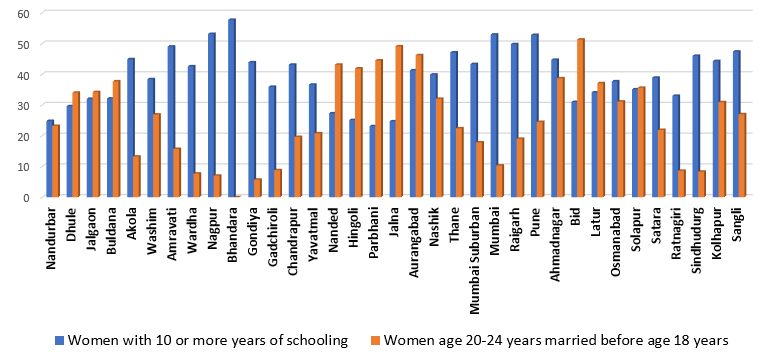
Fig 4. Child Marriage and Girls education across Districts in Maharashtra.
As seen in Fig. 4 above, districts that have more than 50% of girls studying 10 years or more show marked decline in prevalence of Child Marriage.
Women married before 18 years have higher chances of having underweight and stunted children.
The data for Maharashtra is quite revealing on where it exists and how it correlates with issues like Stunting.
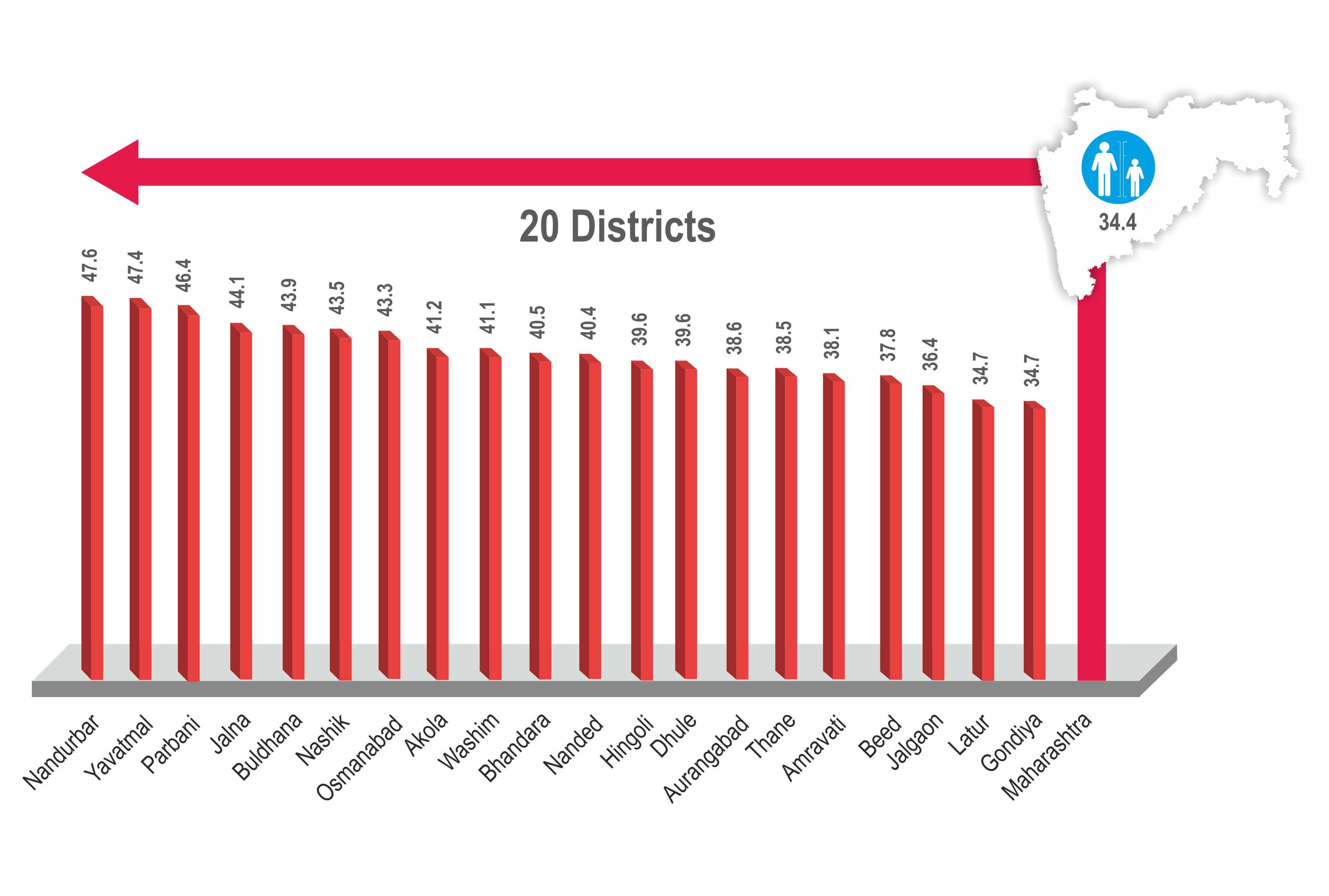
Fig 5. There is co-relation between prevalence of Child Marriage and stunting among children- due to early teenage pregnancies amongst undernourished girls.
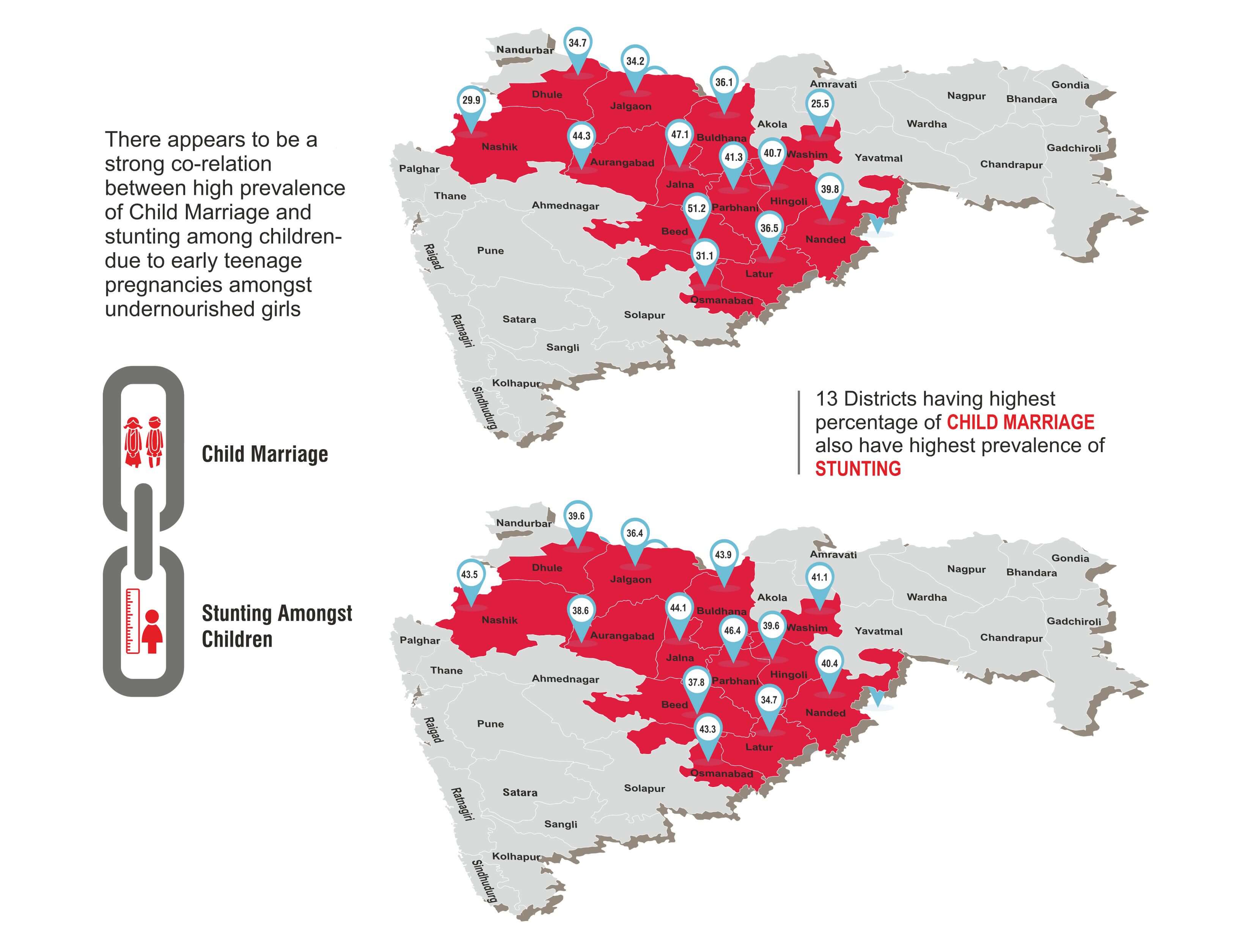
Fig 6. Prevalence of Child Marriage and Stunting
Child marriage is more prevalent among girls with lower levels of education as can be seen in figure below:
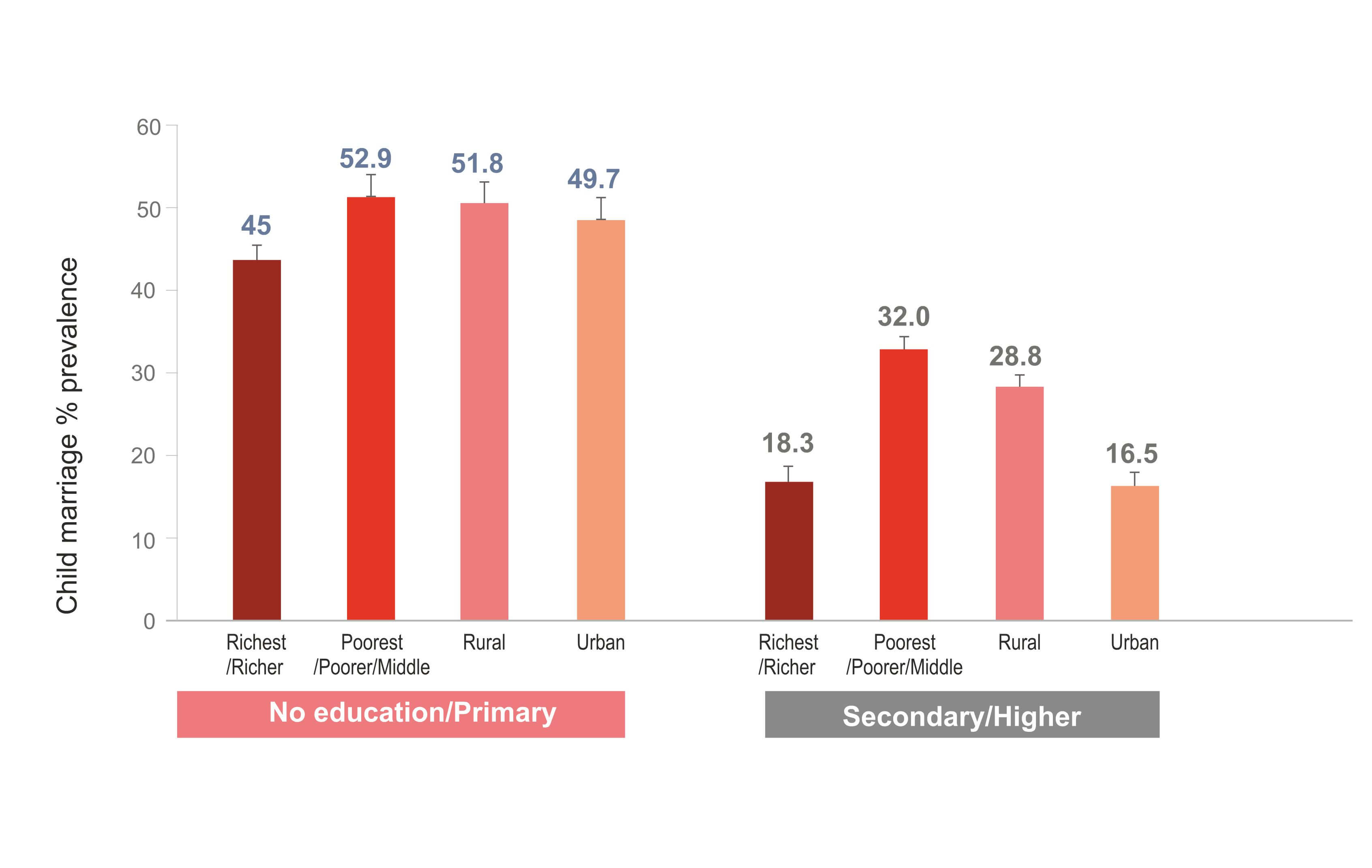
Fig. 7: Percentage of women aged 20 to 24 years who were married before age 18, by education, wealth quintile and residence
The cost to the State’s economy due to child marriages, child stunting, maternal and neo-natal mortality, health care and loss of potential educated & skilled youth is very high.
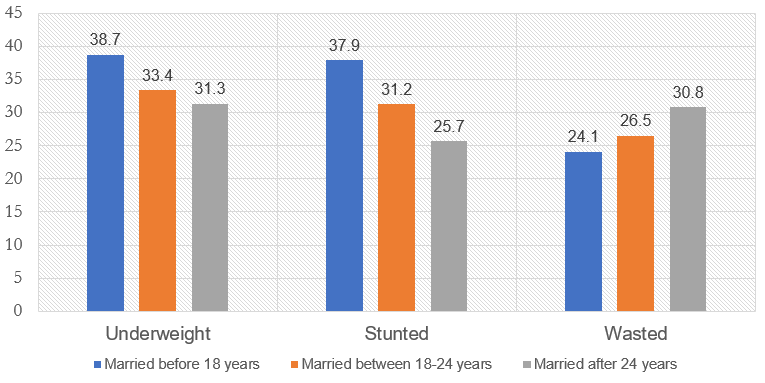
Fig. 8.: Percentage of undernourished children under five years by their mother’s age at marriage.
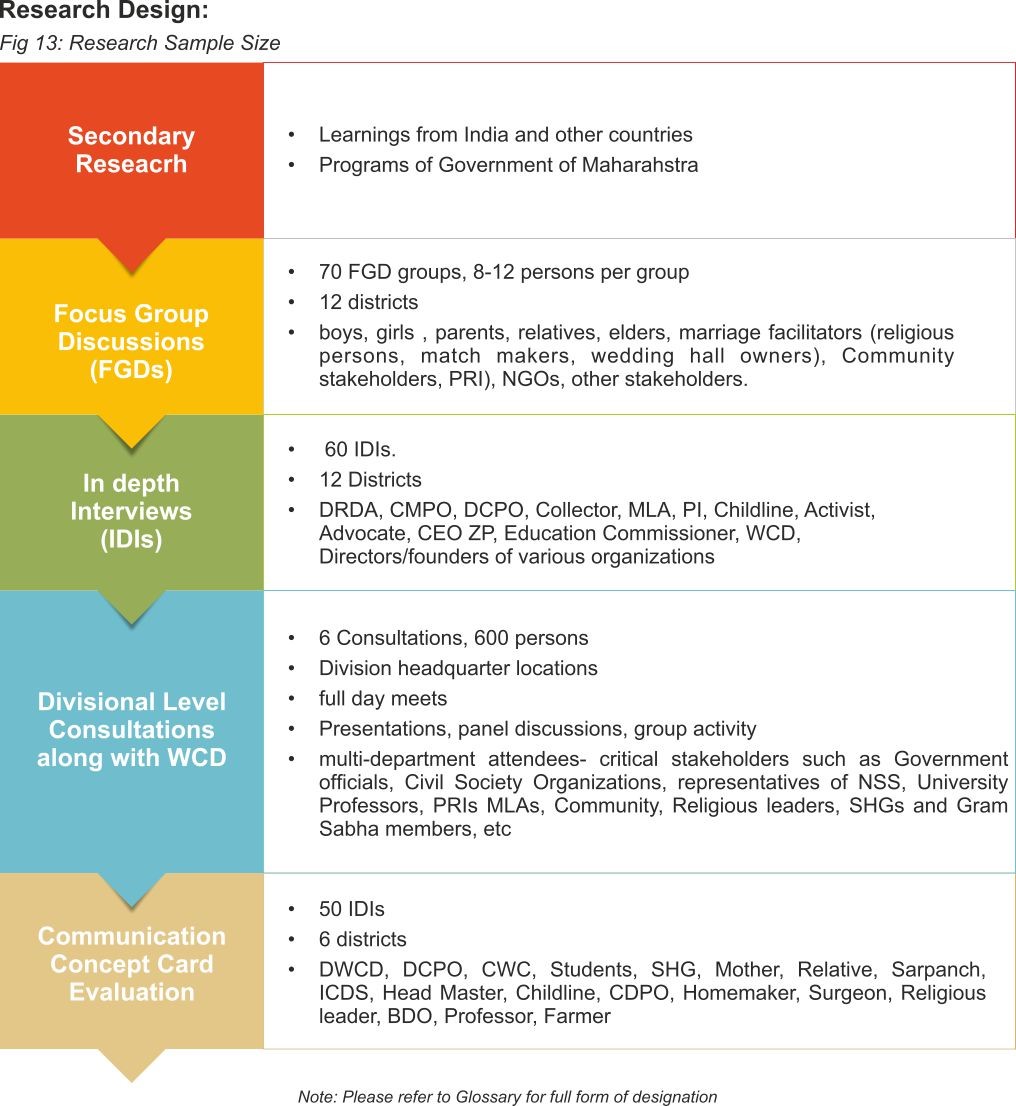
Background: Research, Findings and recommendations for SBCC Strategy for ECM:
During the period September 2018 to April 2019, SBC3 conducted research to determine the direction of SBCC Strategy for Maharashtra.
A three-stage plan was evolved:
- Stage 1: Secondary research covering extensive literature review of studies published on Child Marriage as well as of other documents and strategies on the subject and documenting currently existing schemes and programmes of the Government.
- Stage 2: Qualitative study along with Stakeholder opinion mapping via Consultations
- Stage 3: Analysing and interpreting the findings to develop some key communication concepts and evaluating them to arrive at the final recommendations.

Six communication models/concept cards were developed by the Creative teams. Among the six cards, two alternative cards were for adolescent girls and one each for boys, religious leaders, parents, and the panchayat/village
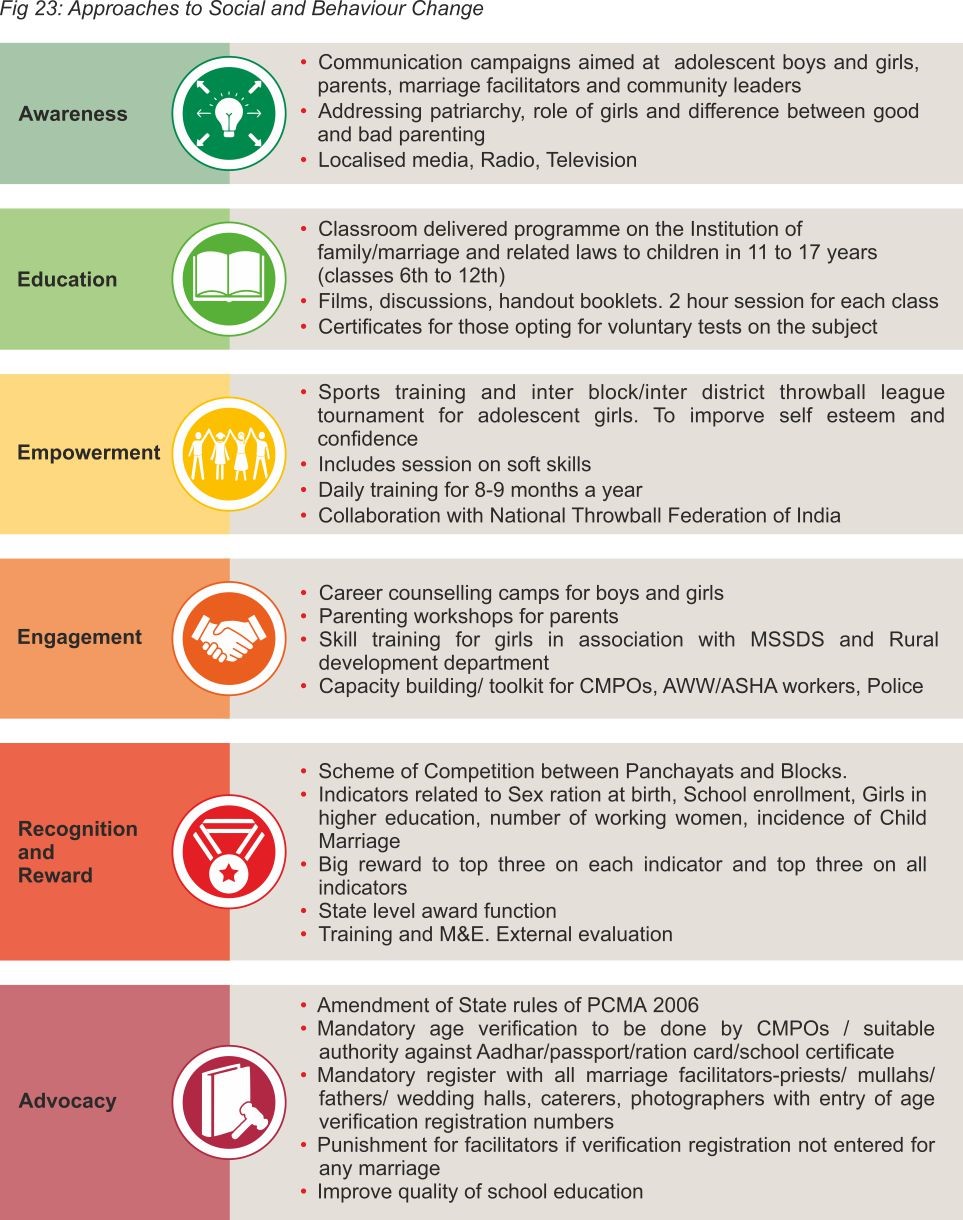
The components of Communication, Law, Administration and Programmes (CLAP) are the six key approaches listed below which form the steps in achieving social and behaviour change needed to end Child Marriage in Maharashtra.
To learn more about our Divisional Consultations on Ending Child marriages through Social and Behaviour Change Strategy please visit:
As part of the next phase, we developed Advocacy Resource Tools comprising:
During the period Nov 2019 to Dec 2019, SBC3 was commissioned to develop Advocacy Resource tools comprising a Film, a book, a brochure and a ppt for use in advocating the issue with the State Government.
SBC3 recommended adopting the following as a programme thematic title:

(Sushikshit, Anubhavi, Kushal, Samaan, Hushar, Udyamshil, Mukt)

Shakshyum Book
Shakshyum PPT for sensitisation and training